Home » About Bone Marrow Transplant
About BMT (Bone Marrow Transplant)
What is Bone Marrow?
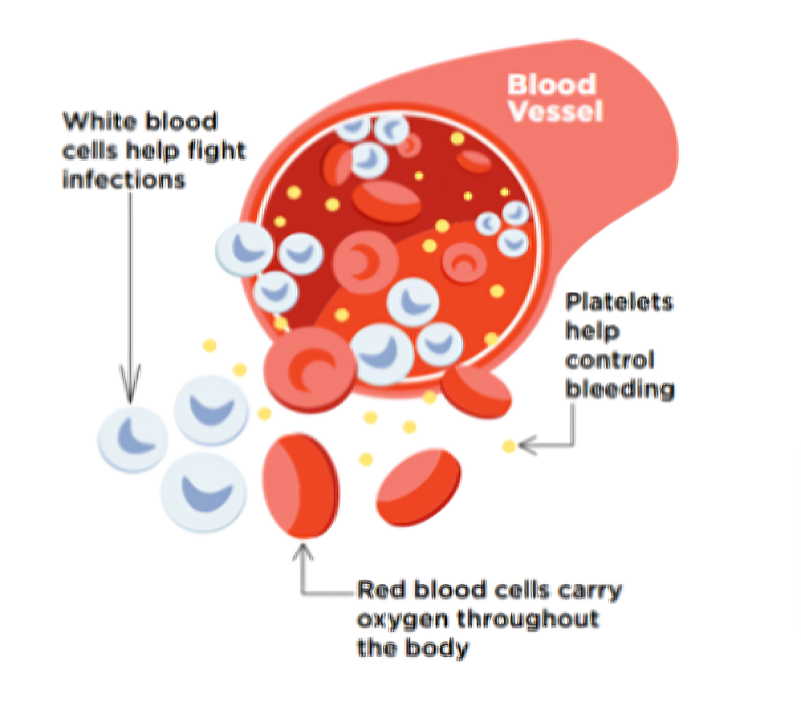
Bone marrow is the pliable, porous substance found within our bones that produces blood-forming cells, also known as blood stem cells. These cells differentiate into various types of blood cells, such as:
- White blood cells for combating infections.
- Red blood cells for transporting oxygen throughout the body.
- Platelets for regulating blood clotting.
What is Bone Marrow Transplant?
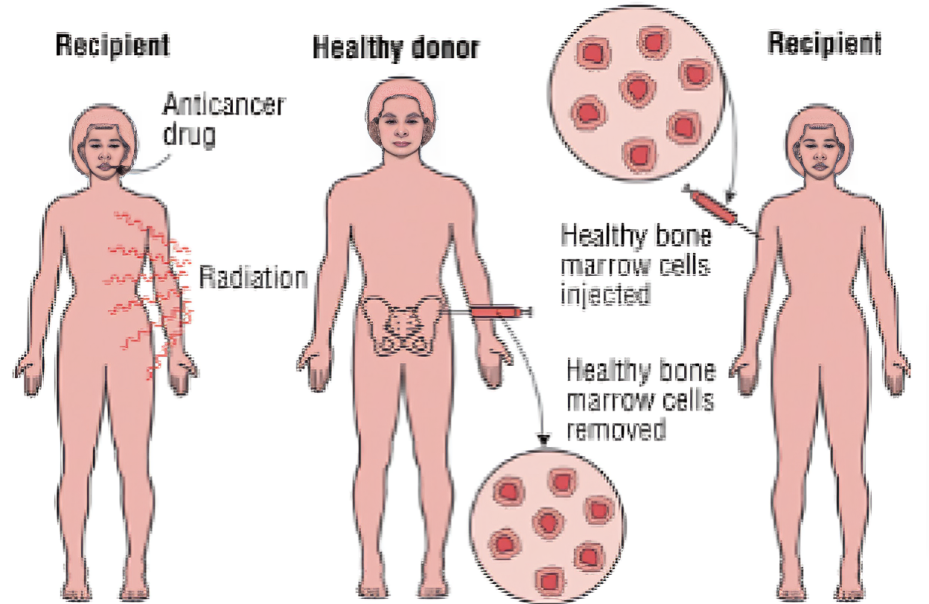
A Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT), also known as a Stem Cell Transplant, is a medical procedure that aims to replace a patient’s damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells from a donor. The bone marrow, which is the soft and fatty tissue found inside our bones, is responsible for producing blood cells. Within the bone marrow, there are immature cells called stem cells that can develop into various types of blood cells. During a BMT procedure, these blood stem cells are transplanted into the patient’s body. Once in the bone marrow, they begin to generate new blood cells and facilitate the growth of new marrow. Ultimately, this process helps the patient regain a normal and healthy life.
What Are The Types of Disease Bone Marrow Transplant Treat?
The field of transplant research is continuously making groundbreaking advancements, enabling the treatment of a wider range of diseases through bone marrow or cord blood transplants. These transplants have proven to be successful in treating and curing various blood cancers, immune system diseases, and blood diseases for a significant period of time. To gain a deeper understanding of how transplant can potentially treat different diseases and determine if it is a viable option for you, visit BMT Clinic.com. It is important to note that for certain diseases, a bone marrow transplant may be the only potential cure available. In fact, there are more than 70 diseases that can be effectively treated through this procedure, and a selection of them is provided on the website.

What Are The Potential Complications And The Corresponding Treatments?

After the stem cell or bone marrow infusion, it typically takes 4 to 6 weeks for the newly transplanted bone marrow to develop and perform its functions properly. This period poses the highest risk of bleeding, infections, and other complications. The complication arises when the transplanted bone marrow, known as the graft, fails to recognize the recipient, referred to as the host. Consequently, the graft releases immune white blood cells, called lymphocytes, to attack the host. The severity of this condition can range from mild to severe, affecting areas such as the skin, liver, or bowel. Symptoms may include rashes and diarrhea, and sometimes biopsies of affected tissues are necessary for diagnosis. This complication is commonly associated with allogeneic transplants, where the donor is either a related or unrelated individual.
Different Types of BMT
The infusion of stem cells, whether obtained from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or cord blood, into the recipient is what Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT) entails. The specific type of bone marrow utilized for the transplant determines the various types of BMT.
Here are the two types of BMT: