Home » Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation » Matched Sibling Donor Transplantation
Matched Sibling Donor Transplantation
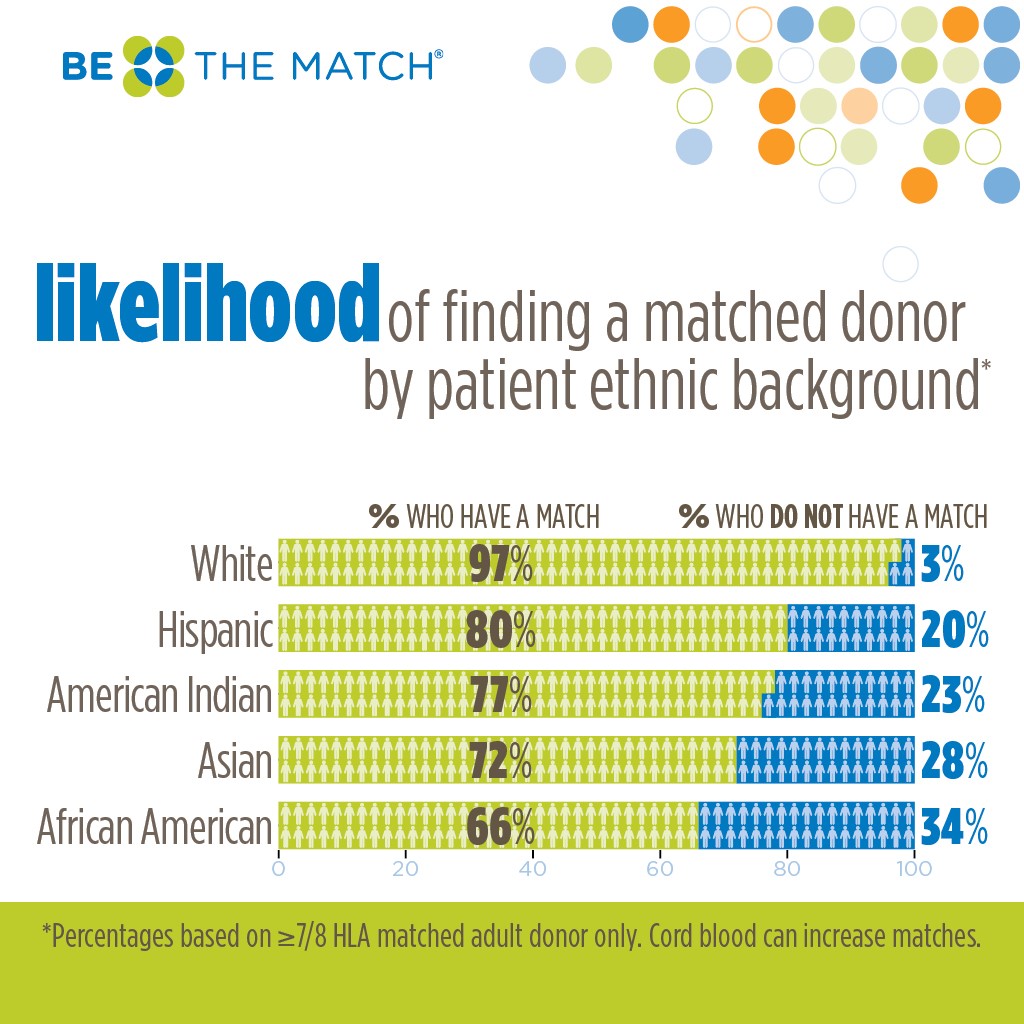
In Allogeneic Transplants, the doctor initially searches for a suitable donor within the patient’s family, typically a brother or sister. This is done by conducting a Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) typing test on both the patient and their siblings who share the same parents. HLA markers are inherited from our parents, and each person has multiple pairs of HLA antigens. The chances of a complete match between the patient and a sibling are 25% (1 out of 4).
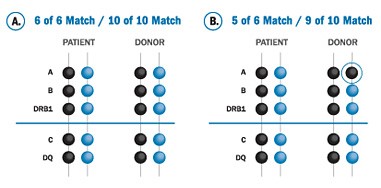
The success rate of a Matched Sibling Donor Transplant is the highest among all types, averaging around 95%. A close HLA match significantly reduces the risk of complications after the transplant, making it the most ideal allogeneic transplant option. However, only 30-40% of patients have access to a Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Matched Sibling Donor (MSD). The degree of match between the donor and recipient’s HLA tissue types greatly influences the success of the transplant. A perfect match occurs when all 10 major HLA antigens are identical, resulting in a 10 out of 10 match. Individuals with such matches have a lower likelihood of experiencing graft-versus-host disease, graft rejection, a weakened immune system, and severe infections.