Home » Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
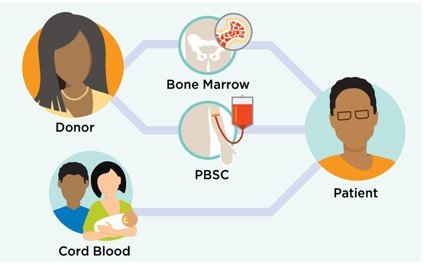
An Allogeneic stem cell transplant or bone marrow involves introducing cells from a donor to the patient. These donated cells have the ability to reproduce, allowing the patient to regain healthy bone marrow and blood. The donor can be a relative, sibling, or an unrelated individual who closely matches the recipient’s genetic makeup. In certain cases, donated blood-forming cells are obtained from umbilical cord blood, which is collected from the umbilical cord and placenta after a baby’s birth.
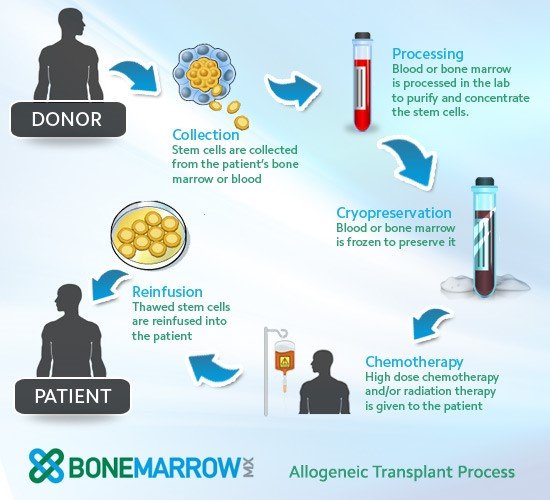
How are patient’s cells collected?
There are four primary types of Allogeneic Transplants:
- Matched Sibling Donor Transplantation: In Allogeneic Transplants, the doctor initially searches for a suitable donor within the patient’s family, typically a brother or sister. This is done by conducting a Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) typing test on both the patient and their siblings who Read More…
- Matched Unrelated Donor Transplantation: Finding a suitable donor can be a difficult and time-consuming task, particularly if there is no sibling who is a match. National and international registries exist where individuals can voluntarily register as potential marrow donors. The search for a bone marrow donor involves looking through these registries to find individuals whose blood closely matches or resembles that of the person in need of a Read More..
- Haploidentical Family Donor Transplantation: Haploidentical or half-matched donor bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is the sole available treatment option for individuals with blood disorders who have been recommended for BMT but lack a fully HLA-matched family donor or a matched unrelated donor. A Haploidentical Transplant is a form of Allogeneic Transplant that utilizes healthy blood-forming cells from a half-matched donor to Read More…
- Unrelated Cord Blood Transplantation: This information is intended for patients or parents who are contemplating umbilical cord blood transplantation. It provides an overview of the procedure and outlines any potential risks or side effects. In some cases, individuals receive blood-forming cells from donated umbilical cord blood, which is collected from the umbilical cord and placenta following a baby’s birth. The stem cells undergo testing, typing, counting, and freezing until they are prepared for Read More…
Need Help in BMT?
Fill this form Below
